
to Antioxidants
II. Benefits of Antioxidants
III. Types of Antioxidants
IV. Foods High in Antioxidants
V. How to Get Enough Antioxidants
VI. Side Effects of Antioxidants
VII. Antioxidants and Cancer
VIII. Antioxidants and Heart Disease
IX. Antioxidants and Aging
General Questions
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Antioxidant | A substance that protects cells from damage caused by free radicals. |
| Boost | To increase the amount of something. |
| Colorful fresh juices | Juices made from fruits and vegetables that are brightly colored. |
| Nourish | To provide with the food or other substances that are necessary for growth and health. |
| Vegetable juice | Juice made from vegetables. |
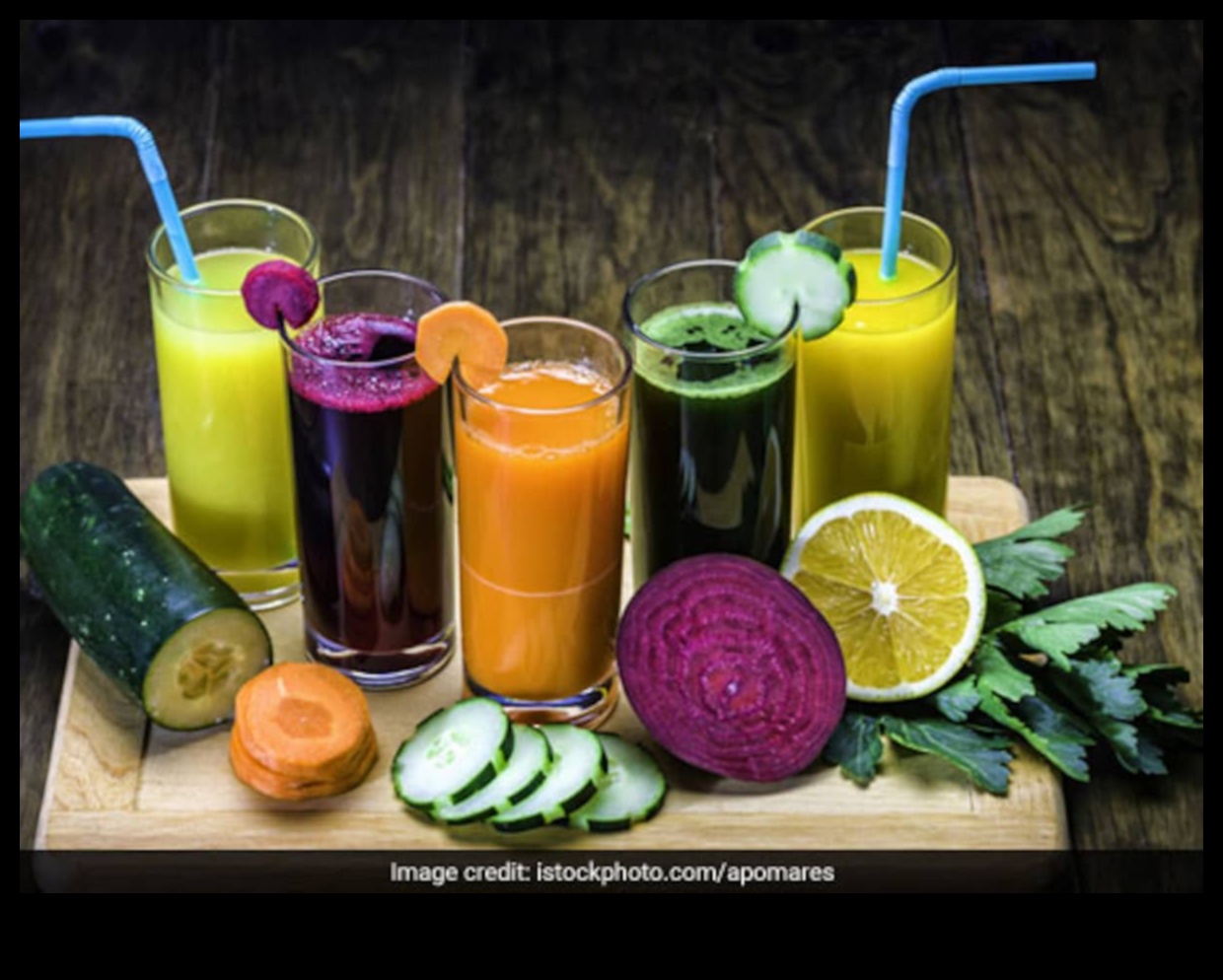

II. Benefits of Antioxidants
Antioxidants are molecules that protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that are formed as a byproduct of metabolism. They can also be produced by environmental factors such as pollution and smoking. When free radicals accumulate in the body, they can damage cells and contribute to the development of chronic diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and aging.
Antioxidants can help to neutralize free radicals and protect cells from damage. This can help to reduce the risk of chronic diseases and promote overall health and well-being.
III. Types of Antioxidants
There are many different types of antioxidants, each with its own unique properties. Some of the most common types of antioxidants include:
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin E
- Beta-carotene
- Lycopene
- Selenium
- Flavonoids
- Polyphenols
These antioxidants work by neutralizing free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can damage cells and lead to a number of health problems. By preventing or slowing down the damage caused by free radicals, antioxidants can help to protect the body from a variety of diseases, including cancer, heart disease, and stroke.
Antioxidants are found in a variety of foods, including fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds. Eating a diet rich in antioxidants is one of the best ways to protect your health and well-being.
IV. Foods High in Antioxidants
Antioxidant-rich foods include:
- Fruits: berries, cherries, grapes, oranges, apples, peaches, pears
- Vegetables: leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, tomatoes, carrots, sweet potatoes
- Nuts and seeds: almonds, walnuts, pecans, pistachios, sunflower seeds, pumpkin seeds
- Whole grains: brown rice, oats, quinoa, barley
- Beans and legumes: lentils, chickpeas, black beans, pinto beans
- Fish: salmon, tuna, mackerel, sardines
- Dark chocolate
These foods are all good sources of vitamins, minerals, and fiber, in addition to antioxidants. Eating a diet rich in antioxidant-rich foods can help to protect your body from damage caused by free radicals and promote overall health and well-being.
V. How to Get Enough Antioxidants
There are many ways to get enough antioxidants in your diet, including:
- Eating a variety of fruits and vegetables
- Choosing whole grains over refined grains
- Consuming nuts and seeds
- Drinking green tea
- Taking a daily multivitamin
It is important to note that not all antioxidants are created equal. Some antioxidants are more powerful than others, and some are better absorbed by the body. For example, beta-carotene is a powerful antioxidant that is found in carrots, sweet potatoes, and other orange-colored fruits and vegetables. However, beta-carotene is not as well absorbed by the body as other antioxidants, such as vitamin C and vitamin E.
When choosing foods to eat for their antioxidant content, it is important to consider the bioavailability of the antioxidants in those foods. Bioavailability refers to the ability of an antioxidant to be absorbed and used by the body. Foods that are high in antioxidants but low in bioavailability will not provide as much benefit as foods that are high in antioxidants and high in bioavailability.
If you are concerned about getting enough antioxidants in your diet, talk to your doctor or a registered dietitian. They can help you create a diet that is rich in antioxidants and that meets your individual needs.

VI. Side Effects of Antioxidants
Antioxidants are generally considered to be safe, but some people may experience side effects such as:
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Headache
- Abdominal pain
- Skin rash
If you experience any of these side effects, stop taking antioxidants and talk to your doctor.

VII. Antioxidants and Cancer
Antioxidants have been shown to have a number of potential benefits for cancer prevention and treatment. Some studies have shown that antioxidants can help to reduce the risk of certain types of cancer, such as lung cancer, prostate cancer, and breast cancer. Antioxidants can also help to slow the growth of cancer cells and improve the effectiveness of cancer treatment.
However, it is important to note that not all studies have found a link between antioxidants and cancer prevention or treatment. Some studies have even suggested that high doses of certain antioxidants may actually increase the risk of certain types of cancer.
More research is needed to determine the exact role of antioxidants in cancer prevention and treatment. However, there is some evidence to suggest that antioxidants may be beneficial for people who are at high risk of cancer or who are undergoing cancer treatment.
If you are interested in taking antioxidants to help prevent or treat cancer, talk to your doctor first. Your doctor can help you determine if taking antioxidants is right for you and can recommend the best types and doses of antioxidants to take.
Antioxidants and Heart Disease
Antioxidants have been shown to help protect against heart disease by reducing inflammation and improving blood flow. Studies have found that people who eat a diet rich in antioxidants have a lower risk of developing heart disease.
Some of the specific antioxidants that have been shown to be beneficial for heart health include:
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin E
- Beta-carotene
- Lycopene
- Flavonoids
In addition to eating a diet rich in antioxidants, you can also improve your heart health by exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, and quitting smoking.
IX. Antioxidants and Aging
Antioxidants are important for maintaining healthy aging. They help to protect cells from damage, and they can also help to reduce inflammation. Some studies have shown that people who consume a diet rich in antioxidants may have a lower risk of developing age-related diseases, such as cancer, heart disease, and Alzheimer’s disease.
There are many different ways to get antioxidants, including eating fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. You can also get antioxidants from supplements. However, it is important to note that not all supplements are created equal. Some supplements may contain high levels of certain antioxidants, which can be harmful. It is important to talk to your doctor before taking any supplements.
Here are some tips for getting enough antioxidants in your diet:
- Eat a variety of fruits and vegetables.
- Choose fruits and vegetables that are brightly colored, as they tend to be higher in antioxidants.
- Eat whole grains instead of refined grains.
- Include nuts and seeds in your diet.
- Limit your intake of processed foods and sugary drinks.
By following these tips, you can help to improve your overall health and well-being and reduce your risk of developing age-related diseases.
General Questions
Q: What are antioxidants?
A: Antioxidants are molecules that protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that are formed as a byproduct of metabolism. They can damage cells and DNA, and contribute to the development of chronic diseases such as cancer and heart disease.
Q: What are the benefits of antioxidants?
A: Antioxidants have been shown to have a number of benefits, including:
- Protecting cells from damage
- Lowering the risk of chronic diseases
- Boosting the immune system
- Promoting healthy aging
Q: What are some good sources of antioxidants?
A: Some good sources of antioxidants include:
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Whole grains
- Nuts and seeds
- Herbs and spices